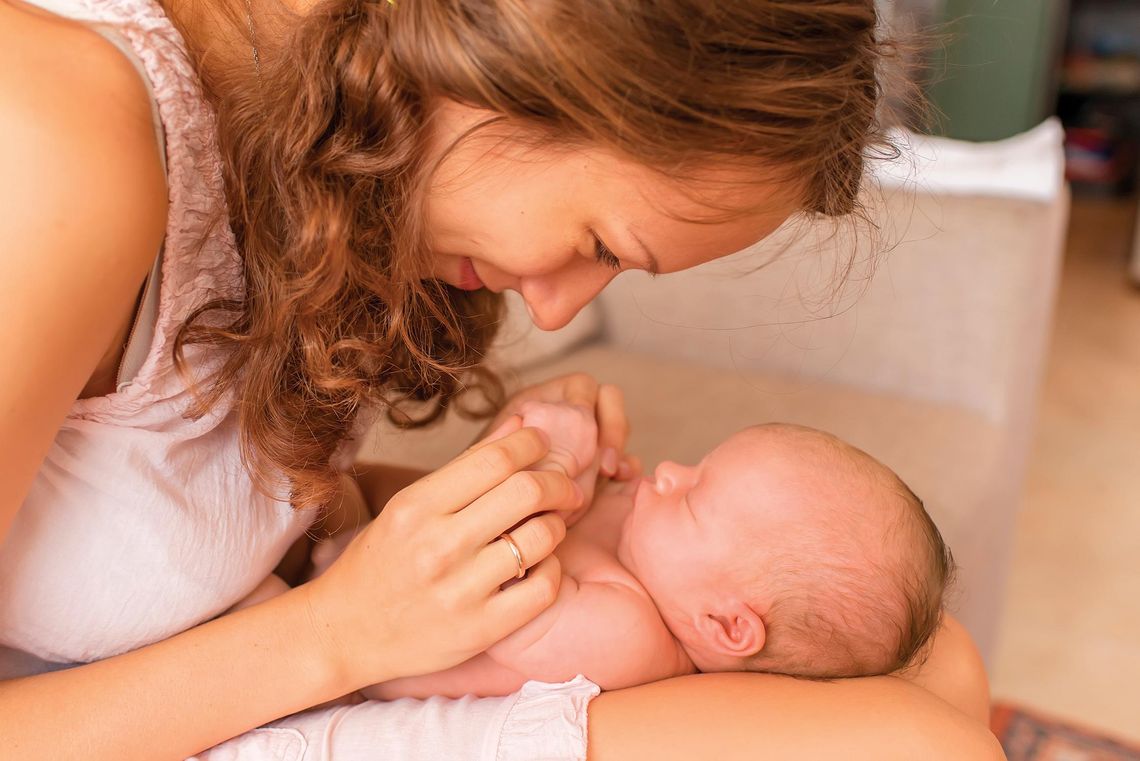
When administered properly, antibiotics can provide essential, even lifesaving, relief to a sick child. However, antibiotics are not without risks.
While they are commonly used to kill bacterial infections or prevent infections from occurring after surgery, overuse and misuse of antibiotics over the past several generations has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The World Health Organization (WHO)calls antibiotic resistance one of the top threats to global health. Since babies are just as susceptible to antibiotic resistance as anyone else, it's critical to educate parents about the risks of antibiotics.
Consider these facts about antibiotic resistance:
- Antibiotic resistance stems from overuse and misuse of antibiotics. According to the CDC, more than 160 million prescriptions are written for antibiotics every year in the United States, and it's estimated 50% of all prescriptions may be inappropriate. It only takes one round of antibiotics to contribute to resistance, and the average child will receive two rounds by age 2. In hospital settings, 40% of newborn infections are now resistant to standard treatment, according to WHO.
- Antibiotic-resistant superbugs spread easily. Antibiotic resistance can spread from humans, farms and animals, and global travel also contributes to the spread of these resistant bacteria. Poor infection control in hospitals is a main factor in the spread of antibiotic resistance, according to the CDC, as bacteria can easily attach to lab coats and medical equipment. These bacterial superbugs have figured out how to survive and spread among humans, creating a vicious cycle that can be difficult and expensive to treat.
- Antibiotic resistance is hard to treat. Superbugs have left doctors and scientists scrambling to find safe alternatives that don't trigger additional resistance. For example, doctors haven been introducing probiotics with B. infantis to fight the spread of antibiotic resistance by reducing harmful bacteria during infancy. Evivo is the first and only clinically proven probiotic for babies.
- Antibiotic resistance can be acquired early in life. Research from Evivo confirms newborns just 7 days old are born with high levels of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and release millions of resistant bacteria in each dirty diaper, further accelerating the spread of antibiotic resistance. In another study conducted by University of California, Davis, with funding from the makers of Evivo, probiotics increased the number of good bacteria. Measuring samples of the babies' feces, they documented a 79 percent increase in levels of bifidobacteria, a type of bacteria that is thought to be protective. At the same time, the scientist noticed a decrease in potentially harmful bacteria such as Clostridium in the babies' guts. The study recruited 68 moms and healthy babies. All of the babies were breastfed. Half of the babies were given the probiotic during the first month of life. The other half — the control group — did not receive a probiotic.
"Since we know that even one round of antibiotics in children can contribute to antibiotic resistance, it's important to take precautionary measures to ensure babies are best prepared in case antibiotics are ever needed," said pediatrician and best-selling nutrition author Dr. Tanya Altmann. "Evivo is the only baby probiotic that is shown to protect baby's gut from bad bacteria, and now it's proven to reduce antibiotic-resistant bacteria before they can multiply or spread to others."
Steps parents can take
Parents can prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria with these practical tips:
- Don't give antibiotics for viral infections such as the common cold or flu.
- If you're unsure whether your child needs an antibiotic, seek information from your health care practitioner about the advantages and disadvantages.
- Follow and complete dosage instructions to ensure bad bacteria are eliminated.
- Don't save antibiotics for next time. If there is any medicine left once you've completed the dosage as prescribed, safely discard the leftovers.